本节包含以下内容:
使用vue-cli脚手架搭建一个项目,项目的主界面搭建vue-router的使用。
1.项目搭建
使用vue-cli的脚手架可以帮助我们快速的搭建一个基于webpack的vue项目,在命令行输入vue init webpack '项目名称',可以快速的创建一个完整的工程。这里一路的敲回车保持默认就可以了。
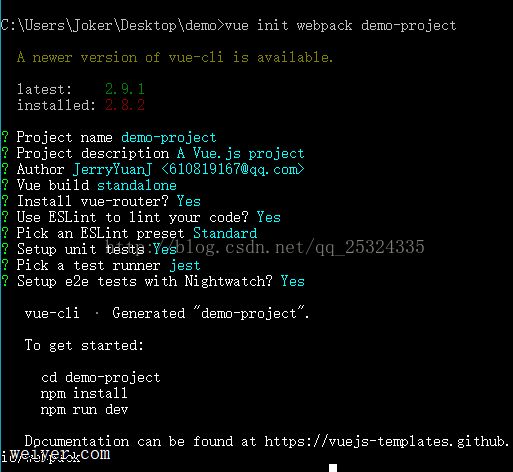
其次我们进入项目根目录,在命令行输入 npm install 进行依赖的安装,如果速度慢的话可以使用cnpm安装。安装过程中遇到莫名其妙的错误可以将node_modules目录删除后重新npm install。
接着我们安装我们本项目需要用到的一些依赖,这里我一次性都安装了,也可以用到哪个安装哪个。要install的有:vuex,axios,mint-ui,echarts,css-loader,style-loader。(以上如果在使用vue-cli创建项目时根据提示安装过的话,不需要再次安装了)。这些依赖安装时是要添加到dependencies里面去的。
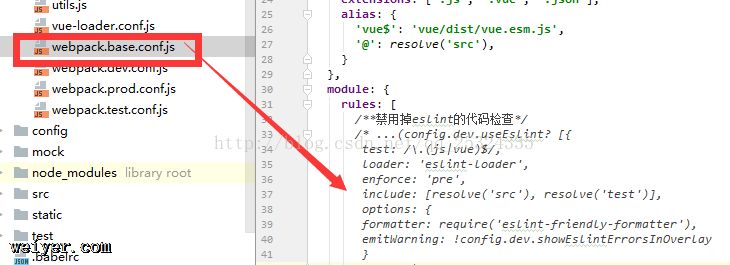
接着我们要配置一下我们的webpack.base.conf.js文件,将里面的eslint代码检查给注释掉,以为我们开发阶段要按照这种规则来编码的话,是很费事的一件事。
接下来在项目根目录下运行 npm run dev就可以运行项目了,运行成功的界面显示如下:

2.项目主界面搭建
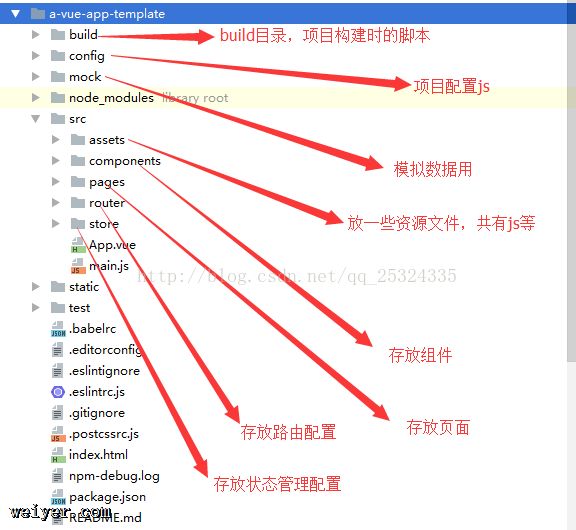
首先,项目的结构目录如下,每个人风格不一样,根据项目组规定来就好了。
由上一节的演示图可以看到,主界面的布局由两部分组成,底部Tab和剩余的显示部分。所以这里我们就需要在App.vue中设置我们的页面,这要用到路由。
不过首先,我们先将底部的Tab抽取出来成为一个组件使用。代码如下:
<template>
<p id="tab-bar">
<mt-tabbar v-model="selected" v-show="isShow" fixed class="border-1px-top">
<mt-tab-item id="main">
<img :src="img1" slot="icon">首页
</mt-tab-item>
<mt-tab-item id="tool">
<img :src="img3" slot="icon">应用中心
</mt-tab-item>
<mt-tab-item id="my">
<img :src="img5" slot="icon">我的
</mt-tab-item>
</mt-tabbar>
</p>
</template>
<style>
</style>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
selected: 'main',
img1: "static/home_selected.png",
img3: "static/tool.png",
img5: "src/assets/logo.png"
}
},
computed: {
isShow: function () {
return true;
}
},
watch: {
'selected': {
handler(){
if (this.selected == "main") {
this.$router.push('/main');
this.img1 = "static/home_selected.png"
} else {
this.img1 = "static/home.png"
}
if (this.selected == "tool") {
this.$router.push('/tool');
this.img3 = 'static/tool_selected.png'
} else {
this.img3 = 'static/tool.png'
}
if (this.selected == "my") {
this.$router.push('/my')
this.img5 = "static/user_selected.png";
} else {
this.img5 = "static/user.png";
}
}
}
}
}
</script>
1.v-show的属性,是用来控制其是否显示的,因为我们的一些界面(比如备忘列表界面)是不需要显示底部tab的,所以这里就要将底部的tab隐藏
掉。这里先写死,后面会有用vuex来进行管理。
2.将selected作为观察者,是因为要处理其显示的改变和进行页面跳转,当某一个tab选中时,进行selected的icon显示。这些逻辑都是在watch里面处理的。
3.fixed是将tabbar固定在底部栏。
底部栏有了以后,我们就要将其作为主界面的一部分应用上去了。具体是修改项目的App.vue文件,代码如下:
<template>
<p id="app">
<p class="content-p">
<!--<transition enter-active-class="animated zoomIn" leave-active-class="animated zoomOut">-->
<router-view/>
<!--</transition>-->
</p>
<footer-bar class="footer"></footer-bar>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import Footer from './components/FooterBar.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
components: {
'footer-bar': Footer
},
computed: {}
}
</script>
<style scoped="">
.content-p {
margin-bottom: 55px;
}
</style>
以main.vue为例,其他类似:
<template>
<p id="index">
首页
</p>
</template>
<style scoped>
#index{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
margin-top: 100px;
}
</style>
<script>
export default{}
</script>
然后将这三个界面配置到router文件夹下的index.js中去:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Main from '../pages/main.vue'
import Tool from '../pages/tool.vue'
import My from '../pages/my.vue'
Vue.use(Router);
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: "/", component: Main
},
{
path: '/main', component: Main
}, {
path: '/tool', component: Tool
}, {
path: '/my', component: My
}
]
})
接着我们修改项目的main.js文件,将路由和其他组件也都引入进来使用。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import MintUI from 'mint-ui'
//import store from './store/index.js'状态管理的,目前还没用上
import echarts from 'echarts'
Vue.prototype.$echarts = echarts
Vue.use(MintUI);
/*Vue.config.productionTip = false;*/
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//store,
template: '<App/>',
components: {App}
});
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="node_modules/mint-ui/lib/style.css">
<title>a-vue-app-template</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="app"></p>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
这时候我们项目的基本结构已经出来了,这时候在项目根路径下npm run dev可以看到如下效果: