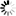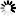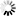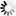Pythonselenium——父子、兄弟、相邻节点定位方式详解,今天跟大家分享下selenium中根据父子、兄弟、相邻节点定位的方法,很多人在实际应用中会遇到想定位的节点无法直接定位,需要通过附近节点来相对定位的问题,但从父节点定位子节点容易,从子节点定位父节点、定位一个节点的哥哥节点就一筹莫展了,别急,且看博主一步步讲解。
1. 由父节点定位子节点
最简单的肯定就是由父节点定位子节点了,我们有很多方法可以定位,下面上个例子:
对以下代码:
parent to child
想要根据 B节点 定位无id的子节点,代码示例如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('D:\\py\\AutoTestFramework\\src\\others\\test.html')
# 1.串联寻找
print driver.find_element_by_id('B').find_element_by_tag_name('p').text
# 2.xpath父子关系寻找
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='B']/p").text
# 3.css selector父子关系寻找
print driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p#B>p').text
# 4.css selector nth-child
print driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p#B p:nth-child(1)').text
# 5.css selector nth-of-type
print driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p#B p:nth-of-type(1)').text
# 6.xpath轴 child
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='B']/child::p").text
driver.quit()
结果:
parent to child parent to child parent to child parent to child parent to child parent to child
第1到第3都是我们熟悉的方法,便不再多言。第4种方法用到了css选择器:nth-child(n),该选择器返回第n个节点,该节点为p标签;第5种方法用到了另一个css选择器: nth-of-type(n),该选择器返回第n个p标签,注意与上一个选择器的区别;第6种方法用到了xpath轴 child,这个是xpath默认的轴,可以忽略不写,其实质是跟方法2一样的。
当然,css中还有一些选择器是可以选择父子关系的如last-child、nth-last-child等,感兴趣可以自行百度,有机会博主会讲讲css selector。
2. 由子节点定位父节点
由子节点想要定位到父节点就有点难度了,对以下代码:
child to parent
我们想要由 C节点 定位其两层父节点的p,示例代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('D:\\py\\AutoTestFramework\\src\\others\\test.html')
# 1.xpath: `.`代表当前节点; '..'代表父节点
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='C']/../..").text
# 2.xpath轴 parent
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='C']/parent::*/parent::p").text
driver.quit()
结果:
child to parent child to parent
这里我们有两种办法,第1种是 .. 的形式,就像我们知道的,. 表示当前节点,.. 表示父节点;第2种办法跟上面一样,是xpath轴中的一个:parent,取当前节点的父节点。这里也是css selector的一个痛点,因为css的设计不允许有能够获取父节点的办法(至少目前没有)
3. 由弟弟节点定位哥哥节点
这是第3、第4种情况,我们这里要定位的是兄弟节点了。如以下源码:
brother 1
brother 2
怎么通过 D节点 定位其哥哥节点呢?看代码示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('D:\\Code\\py\\AutoTestFramework\\src\\others\\test.html')
# 1.xpath,通过父节点获取其哥哥节点
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='D']/../p[1]").text
# 2.xpath轴 preceding-sibling
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='D']/preceding-sibling::p[1]").text
driver.quit()
结果
brother 1 brother 1
这里博主也列举了两种方法,一种是通过该节点的父节点来获得哥哥节点,另外一种比较优雅,是通过 xpath轴:preceding-sibling,其能够获取当前节点的所有同级哥哥节点,注意括号里的标号,1 代表着离当前节点最近的一个哥哥节点,数字越大表示离当前节点越远,当然,xpath轴:preceding也可以,但是使用起来比较复杂,它获取到的是该节点之前的所有非祖先节点(这里不太好解释,改天专门写篇博文讲解下所有的轴)
4. 由哥哥节点定位弟弟节点
源码与 3 一致,要想通过 D节点 定位其弟弟节点,看代码示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('D:\\Code\\py\\AutoTestFramework\\src\\others\\test.html')
# 1.xpath,通过父节点获取其弟弟节点
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='D']/../p[3]").text
# 2.xpath轴 following-sibling
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='D']/following-sibling::p[1]").text
# 3.xpath轴 following
print driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@id='D']/following::*").text
# 4.css selector +
print driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p#D + p').text
# 5.css selector ~
print driver.find_element_by_css_selector('p#D ~ p').text
driver.quit()
结果:
brother 2 brother 2 brother 2 brother 2 brother 2
博主分享了五种方法定位其弟弟节点,上面三种是用xpath,第一种很好理解,第二种用到了xpath轴:following-sibling,跟preceding-sibling类似,它的作用是获取当前节点的所有同级弟弟节点,同样,1 代表离当前节点最近的一个弟弟节点,数字越大表示离当前节点越远;第三种用到了xpath轴:following,获取到该节点之后所有节点,除了祖先节点(跟preceding方向相反,但因为往下顺序容易读,不容易出错,所以也是可以用来获取弟弟节点的,但也不建议这么使用);第四、第五种,我们用到了css selector,+ 和 ~ 的区别是: + 表示紧跟在当前节点之后的p节点,~ 表示当前节点之后的p节点,如果用find_elements,则可获取到一组p节点。