Redux中文文档中有这么一句话:
这里需要再强调一下:Redux 和 React 之间没有关系。Redux 支持 React、Angular、Ember、jQuery 甚至纯 JavaScript。
不得不说这句话极大的鼓舞了我,Redux作为一款前端状态管理工具本质上和特定框架是解耦的。如果业务有需求,我们当然可以也引入到其他框架,比如说我们项目用的Angular2。
当初怀着这样的心情查找了一下,果然Angular2也推出了对Redux的实现:ngrx。试着用了一下,觉得效果也挺好。
ngrx介绍
RxJS powered state management for Angular applications, inspired by Redux
@ngrx/store is a controlled state container designed to help write performant, consistent applications on top of Angular. Core tenets:
State is a single immutable data structure Actions describe state changes Pure functions called reducers take the previous state and the next action to compute the new state State accessed with the Store, an observable of state and an observer of actions上述前三点其实就是Redux的规则,而最后一条却是ngrx的特色。这个稍后展开。
Redux中文文档中用React作为示例框架,自然在用法上和ngrx有一些不同,而我认为这种不同不单单是使用上的,而且反应出两种框架不同的设计思想,这也是我想整理一下记录下来的原因。
先写几点目前水平能看到的,随着深入使用会不定期的补充。
Redux 如何接入框架
这个问题换一种问法就是Redux中的store是如何被React/Angular2拿到的?
React:
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import App from './containers/App';
const store = createStore(rootReducer, initialState);
render(
,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Angular2:
import { Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import * as fromRoot from '../reducers';
@Component({
selector: ...,
template: ...,
style: ...
})
export class AppComponent {
// store 通过依赖注入
constructor(private store: Store) {
this.showSidenav$ = this.store.select(fromRoot.getShowSidenav);
}
}
从上面两段代码可以看出,React是在App根组件上面又包裹了一层Provider,通过Provider引入store,之后作为props的一部分传递给所有子组件。而Angular2相对简单一些,store直接注入到根组件中,就像注入一个普通的service一样。
从对引入store用法上的不同其实是可以看出Angular2和React设计理念的不同:React的设计初衷是作为MVC中的View层,至于其他部分,更多的是依赖生态系统的提供。所以React整合Redux更多的是从View层面着手,反映到使用方式上就是在根组件上再加一层。而Angular2的设计理念是提供一整套方案涉及到MVC的各方面,在引入http,route此类工具的时候就是通过依赖注入,在整合Redux时也没有例外。 依赖注入本来就是Angular2架构中非常关键的一环。
异步数据流
默认情况下,createStore() 所创建的 Redux store 没有使用 middleware,所以只支持 同步数据流。
React:
像 redux-thunk这样支持异步的 middleware 都包装了 store 的 dispatch() 方法,以此来让你 dispatch函数,在该函数中实现异步的逻辑。
Angular2:
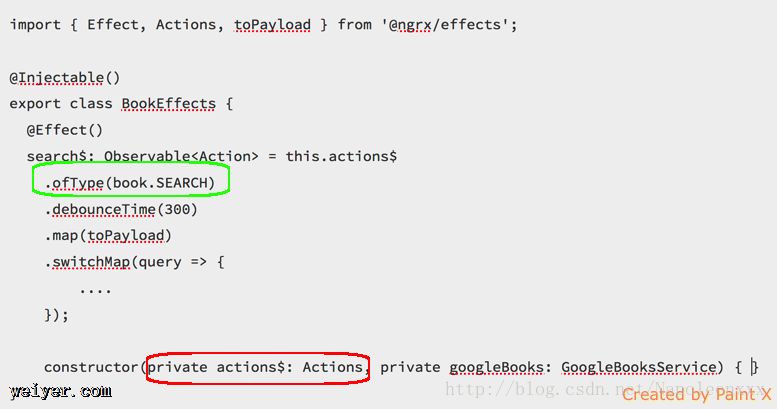
在ngrx中你是找不到类似于ngrx-thunk的东西的。ngrx另辟蹊径,提出了一个叫做<@Effect的装饰器: 它来帮助我们检查 store 发出的 Action,将特定类型的 Action 过滤出来进行处理。当发现特定的 Action 发出之后,自动执行某些异步操作(比如执行异步请求回调),然后将处理的结果重新发送回 store 中。
Effects offer a way to isolate and easily test side-effects within your application.

可以看出,thunk的做法是扩展action,使其可以支持函数,然后在函数中操作异步逻辑,而在ngrx中,action始终还是那个简单的action,通过Effect装饰器类来监听action并作出相应的动作。这样的优点我觉得是实现了同步数据流和异步数据流解耦,代码层次更加清楚。
所以我觉得RxJs天生就和Redux完美匹配,Redux只关心在正确的时候dispatch正确的action,处理state的逻辑交给reducer,同步异步的管理交给RxJs.
Effect的技术核心是RxJs响应式编程思想。这一小节主要是从代码结构角度。下一小节将会从Observable的角度来谈。
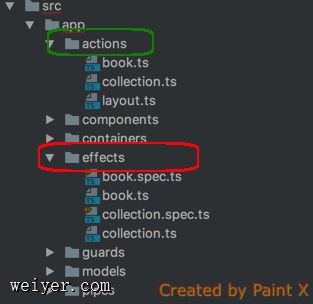
ngrx = Redux + RxJs
RxJs并不是Redux中的范畴,Angular2中有对RxJs的强大实现,ngrx很好的利用了这套支持,实现了一个响应式的Redux,使得Redux的功能在Angualr2中更加强大,使用更加简练。
注:Redux社区现在也提供了Redux-Observable中间件。
根据之前的代码可以看出,Effect中用actions$.ofType(specific-action)来监听特定的action dispatch的行为。而实现这一步的关键:make actions observable 是关键,只有将actions变成数据流(stream),我们才可以利用RxJs赋予的强大功能。
本小节的内容可以看作是对Effect的深入探究:make action observable:
actions.ts:
import { Action } from '@ngrx/store';
// 实现ngrx中的Action接口,将普通的action对象放入stream
export class SearchAction implements Action {
readonly type = SEARCH;
constructor(public payload: string) { }
}
effect.ts:
search.ts
import { Store } from '@ngrx/store';
@Component({
selector: 'bc-find-book-page',
template: `
) {
//.....
}
search(query: string) {
this.store.dispatch(new book.SearchAction(query));
}
}
代码中可以看出store已经是observable了,当store dispatch一个action的时候,相当于向actions stream发出了一个执行指令。actions stream通过调用ofType这个operator将action导入到相应的处理逻辑。