核心提示:既然说到伪类,这里就用足够的代码给表现一下他们的神奇用法。从简单到复杂,可以清晰的看清到伪类的诸多使用方法,对于有些功能近似的就取其一举例了::first-letter为第一个字添加样式,这里用一个首...
既然说到伪类,这里就用足够的代码给表现一下他们的神奇用法。从简单到复杂,可以清晰的看清到伪类的诸多使用方法,对于有些功能近似的就取其一举例了:
:first-letter
为第一个字添加样式,这里用一个首字下沉的例子来演示一下:
<!--html部分-->
<p>中国是以华夏文明为源泉<!--内容省略--></p>
<!--css部分-->
p:first-letter{
display: block;
float: left;
margin-right: .2em;
font-size: 1.7em;
}

:first-line
为段落的第一行添加样式:
<!--html部分-->
<p style="text-align: center;">
锦瑟<br/>
锦瑟无端五十弦,一弦一柱思华年。<br/>
庄生晓梦迷蝴蝶,望帝春心托杜鹃。<br/>
沧海月明珠有泪,蓝田日暖玉生烟。<br/>
此情可待成追忆?只是当时已惘然。<br/>
</p>
<!--css部分-->
p:first-line{
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 1.7em;
}

::selection (CSS3)
设置文字被选中是的状态,还是上面那段文字:
<!--css部分-->
.select::selection{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}

:empty (CSS3)
内容为空的元素样式
<!--html部分-->
<p></p>
<p>我有内容</p>
<!--css部分-->
p{
width: 60px;
height: 40px;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 5px;
}
p:empty{
background-color: darkgray;
}

如果<a></a>中间没有内容,把href的值作为内容:
<!--html部分-->
<a href="www.baidu.com"></a>
<!--css部分-->
a:empty:before{
content: attr(href);
}
:focus
当元素获得焦点时的样式
<!--html部分-->
<input tyle="text" />
<!--css部分-->
input[type="text"]:focus{
border: 1px purple solid;
box-shadow: 0 0 15px black;
}
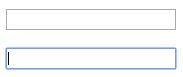
:disabled (CSS3)
被禁用元素的样式
<!--html部分-->
<input tyle="text" disabled />
<!--css部分-->
input[type="text"]:disabled{
background-color: #555555;
}

:link :hover :active :visited
:link 锚点的样式
:hover 鼠标浮动在元素上方时的样式(任何元素)
active 鼠标点击下去的样式(任何元素)
:visited 鼠标点击过后的颜色(任何元素)
<!--html部分-->
<a href="www.baidu.com">百度</a>
<!--css部分-->
a:link{
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: black;
}
a:hover{
text-decoration: underline;
color: blue;
}
a:active{
text-decoration: none;
color: purple;
}
a:visited{
text-decoration: none;
color: darkgray;
}

:first-child :last-child :nth-child(n) :not(selector)
:first-child 第一个元素样式
:last-child 最后一个元素样式
:nth-child(n) 第n个元素样式(这个还能玩出花样的)
:not(selector) 不符合selector选择器的样式
<!--html部分省略,一个10元素的ul,其中第四个li的name属性为except-->
<!--css部分-->
ul li{
list-style: none;
background-color: skyblue;
color: white;
text-align: center;
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
margin: 5px auto;
float: left;
}
ul li:first-child{
color: blue;
}
ul li:last-child{
color: red;
}
ul li:nth-child(3){
color: darkgreen;
}
ul li:not([name="except"]){
font-style: italic;
}
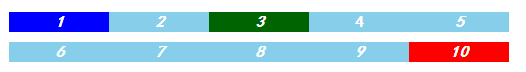
<!--css部分-->
/*下面实现偶数部分样式变化*/
ul li:nth-child(2n){ /*2n+1可以表示奇数的*/
background-color: blue;
}
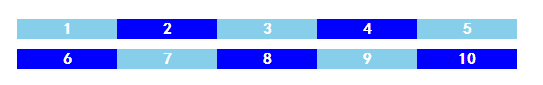
<!--css部分-->
/*下面实现连续部分样式变化*/
ul li:nth-child(n+3):nth-child(-n+8){
background-color: blue;
}
/*
:nth-child(n+3)表示第三个以后的元素
:nth-child(-n+8)表示第8个以前的元素
因此这里选择了选择第三到第八的元素
*/

此外CSS3中:first-of-type :last-of-type :nth-of-type(n) :nth-last-of-type(n)用法与上述相似,作用也一致,其中:nth-last-of-type(n)表示倒数第n个元素
还有:only-child和CSS3中的:only-of-type两个伪类,表示单独的元素,也就是前后没有与之相同的元素。
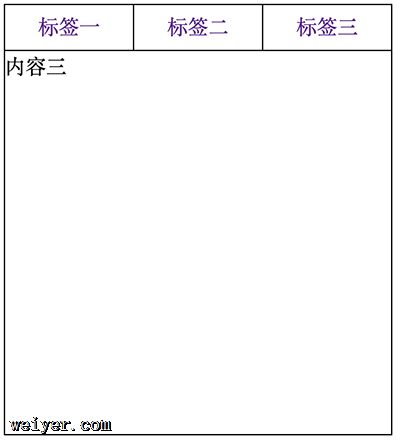
:target
:target 选择器可用于选取当前活动的目标元素(即url中的锚元素)。
下面用target做一个选项卡的样式(点击切换)
<!--html部分-->
<p id="tab">
<nav class="title">
<a href="#a">标签一</a>
<a href="#b">标签二</a>
<a href="#c">标签三</a>
</nav>
<ul class="content">
<li id="a">内容一</li>
<li id="b">内容二</li>
<li id="c">内容三</li>
</ul>
</p>
<!--css部分-->
#tab .title a{
float: left;
text-decoration: none;
width: 100px;
height: 35px;
line-height: 35px;
text-align: center;
border:1px solid black;
}
#tab .title a:nth-child(n+2){
border-left:none;
}
#tab .content{
clear:both;
position:relative;
}
#tab .content li{
width:302px;
height:300px;
border:1px solid black;
border-top: none;
background-color: white;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top:0;
}
#tab .content li:target{
z-index:1;
}
:before :after
这个是最值得一提的,在元素的前后添加内容,当然也可以添加一个块元素,这个块变化就无穷了,下面举几个例子:
首当其冲的就是清除浮动了
<!--html部分-->
<p class="clr">
<p class="float">1</p>
<p class="float">2</p>
</p>
<p class="float">3</p>
<p class="float">4</p>
<!--css部分-->
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.float{
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: blue;
margin: 5px;
float: left;
color: yellow;
}
.clr:after{
content: "";
clear: both;
overflow: hidden;
height: 0;
display: block;
}
<!--html部分-->
<p class="new"><img src="pic/test.jpg" /><span>new</span></p>
<!--css部分-->
.new,img{
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
.new span{
position: relative;
display: block;
letter-spacing: 2px;
font-size:20px;
width:30px;
height:20px;
color: white;
top: -190px;
left: 262px;
z-index:1;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
.new:after{
content:"";
display:block;
font-size:20px;
width: 0;
height: 0;
border:solid 35px transparent;
border-top-color: red;
border-right-color: red;
position:relative;
top: -224px;
left: 230px;
}

<!--html部分-->
<p class="enlarge button">按钮</p>
<!--css部分-->
.button{
width:80px;
height: 40px;
border:2px solid dimgray;
background-color: dodgerblue;
color: #202020;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
font-size: 20px;
margin:20px;
}
.enlarge:after{
content:"";
display: block;
height: 60px;
width: 100px;
position: relative;
top: -50px;
left: -10px;
background-color: rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.4);/*用颜色表示一下区域,应该透明*/
}

<!--html部分-->
<p class="cor_num button" data-num="8">按钮</p>
<!--css部分-->
.cor_num:after{
content: attr(data-num);
padding:0;
line-height: 22px;
position: relative;
display: block;
background-color: red;
top: -50px;
left: 68px;
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
border-radius: 12px;
color: white;
font-size:14px;
}

<!--html部分-->
<p class="dialog">这是一个对话框</p>
<!--css部分-->
.dialog{
background-color: pink;
border: 2px solid gray;
text-align: center;
line-height: 80px;
width: 150px;
height: 80px;
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.dialog:after{
content:"";
display: block;
background: inherit;
border: inherit;
border-top: 0;
border-left: 0;
position: relative;
width:30px;
height: 30px;
top: -15px;
left: 20px;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}

<!--html部分-->
<p class="luck"><span>福</span></p>
<!--css部分-->
.luck{
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin:30px;
margin-bottom: 45px;
}
.luck span{
color: gold;
position: relative;
font-size: 4em;
width:70px;
height: 70px;
transform: rotate(180deg);
display: block;
top: -80px;
left: 16px;
}
.luck:before{
content:"";
display:block;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}