react组件在生命周期里大概有三种情况:
初次渲染:组件第一次在dom树种渲染。重新渲染:状态更新导致再次渲染。卸载:组件从dom中删除
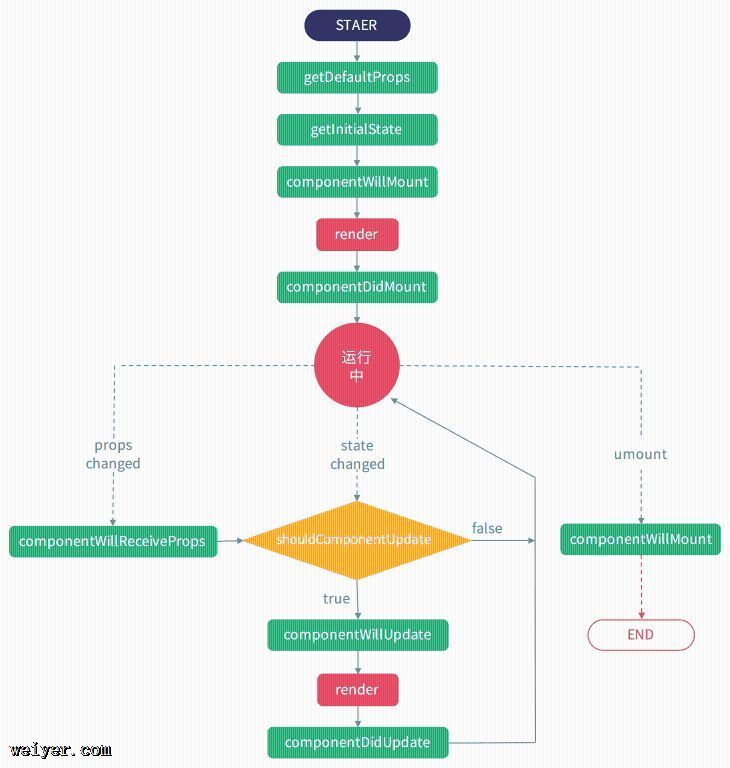
在写三种渲染情况之前,先来说下常用的八大生命周期(16.3之前)
1.componentWillMount()
执行场景
在 render() 之前
解释因为componentWillMount是在render之前执行,所以在这个方法中setState不会发生重新渲染(re-render)
通常情况下,推荐用constructor()方法代替
2.render()
执行场景
在componentWillMount() /constructor() / componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps)之后
3.componetDidMount()
执行场景
在 render()之后
解释
在 render() 之后立即执行
如使用 redux / mobx 等状态管理,可在此方法内加载数据注意
可调用 setstate(),但是并不推荐在此方法内执行setstate() ,会存在阻塞 例如:
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
val: 0
};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val); // 第 1 次 log
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val); // 第 2 次 log
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val); // 第 3 次 log
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val); // 第 4 次 log
}, 0);
}
render() {
return null;
}
};
输出为 0 0 2 3
4.componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps)
执行场景
在接收到新的props时
解释在props传入时props或props发生变化时,触动此方法,此时可能会需要比对初始props和nextProps,避免无谓的渲染
注意以下是使用旧版(16.3之前)componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps) 生命周期基于新的道具值更新状态的组件示例:
// Before
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
isScrollingDown: false,
};
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if (this.props.currentRow !== nextProps.currentRow) {
this.setState({
isScrollingDown:
nextProps.currentRow > this.props.currentRow,
});
}
}
}
尽管上面的代码本身并没有问题,但componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps) 生命周期可能会多次调用但是只更新一次。因此,该方法将被弃用。16。3之后版本会变更为UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps,17版本移除
5.shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
执行场景
接受到新的props或state, 在componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps)之后
解释
默认返回true,重新渲染,返回false时阻止渲染