页面架构
CSS Reset
原因?
浏览器会对标签进行默认设置,通过标签进行设置,是全局性的。浏览器之间的设置可能不一样。对我们来说,很多默认样式都没有用,不能满足要求,还需要额外去覆盖。
如何设置?
覆盖,清除;注意新标签在低版本浏览器里面的兼容性;全局性的样式定义;设置后引入。
什么是Reset?
清除默认样式,不同项目可能需要不同的Reset;全局性的样式设定。
Reset First,
项目初期就应该缺点;引入时应该放在第一位;没有标准答案,不同产品需求不同,符合自己产品的Reset才是最好的Reset。
网易推荐的Reset 规范:
html,body,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,p,dl,dt,dd,ul,ol,li,p,blockquote,pre,hr,figure,table,caption,th,td,form,fieldset,legend,input,button,textarea,menu{margin:0;padding:0;}
header,footer,section,article,aside,nav,hgroup,address,figure,figcaption,menu,details{display:block;}
table{border-collapse:collapse;border-spacing:0;}
caption,th{text-align:left;font-weight:normal;}
html,body,fieldset,img,iframe,abbr{border:0;}
i,cite,em,var,address,dfn{font-style:normal;}
[hidefocus],summary{outline:0;}
li{list-style:none;}
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,small{font-size:100%;}
sup,sub{font-size:83%;}
pre,code,kbd,samp{font-family:inherit;}
q:before,q:after{content:none;}
textarea{overflow:auto;resize:none;}
label,summary{cursor:default;}
a,button{cursor:pointer;}
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,em,strong,b{font-weight:normal;}
del,ins,u,s,a,a:hover{text-decoration:none;}
body,textarea,input,button,select,keygen,legend{font:30px/1.5 'microsoft yahei';color:#333;outline:0;}
body{background:#fff;}
a,a:hover{color:#333;}
.parent{background:#ddd;}
.child{background:#666;color:#fff;}
布局解决方案
居中布局
水平居中
背景html代码:
DEMO
inline-block+text-align;子元素设置display:inline-block:宽度根据内容变化
text-align:对inline元素起作用;
缺点在于影响所有元素;
兼容性非常好;
display:inline,zoom:1兼容ie6 7
.parent{
text-align: center;
}
.child{
display: inline-block;
}
table + margin
子元素设置display:table,table非常像block,但是宽度会随着内容变化;
子元素设置margin:0 auto;
优点在于只设置child,不影响父元素;
.child{
display: table;
margin: 0 auto;
}
absolute +transform
子元素设置position:absolute;
父元素设置position:relative;
absolute默认没有宽度,宽度由父元素决定;
子元素:left:50%;
子元素:transform:translateX(-50%);(百分比为自身的宽度);
优点在于脱离文档流,不影响别的元素,缺点在于兼容性;
.parent{
position: relative;
}
.child{
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
}
flex + justify-content
父元素:display:flex;justify-content:center;
或者子元素:margin:0 auto;
优点在于只需要设置父元素,缺点在于兼容性;.parent{ display: flex; justify-content: center; } .child{ margin: 0 auto; }
垂直居中
table-cell + vertical-aligndisplay:table-cell;转换为单元格;
兼容性好:可以兼容到ie8;
.child{width:100%;}
.parent{
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
absolute+transform
优点是子元素不会干扰其它元素,缺点在于兼容性;
.parent{ position: relative; } .child{ position: absolute; top: 50%; transform: translateY(-50%); }
flex + align-items
只需要设置parent的属性,缺点在于兼容性;
.parent{
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
水平垂直都居中
inline-block + text-align + table-cell + vertical-align;
.parent{
text-align: center;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.child{
display: inline-block;
}
absolute + transform;
.parent{
position: relative;
}
.child{
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}
flex + justify-content + align-items;
.parent{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
多列布局
定宽+自适应float:+margin-left;容易理解兼容性有一点问题,ie6里面,3像素bug;
.parent{
}
.left{
float: left;
width: 100px;
}
.right{
margin-left: 120px;
}
改进:左右皆浮动;position:relative;层级提高;
.parent{
}
.left{
float: left; width: 100px;
position: relative;
}
.right-fix{
float: right; width: 100%;
margin-left: -100px;
}
.right{
margin-left: 120px;
}
overflow-hidden;触发bfc模式,和外界隔离;ie6下不支持;
.parent{
}
.left{
float: left;
width: 100px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
overflow: hidden;
}
display:table;子元素:table-cell,定长为总宽度;父元素,table-layout;不支持margin,支持padding;
.parent{
display: table; width: 100%;
table-layout: fixed;//固定表格布局,相对自动表格布局,提高了浏览器运行效率
}
.left,.right{
display: table-cell;
}
.left{
width: 100px;
padding-right: 20px;
}
父元素:display:flex:子元素flex:1
.parent{
display: flex;
}
.left{
width: 100px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
flex: 1;
}
定宽+定宽+自适应
.parent{
}
.left,.center{
float: left;
width: 100px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
overflow: hidden;
}
不定宽+自适应
float + overflow,在ie6存在兼容性问题;
可任意改变左列宽度,右边不受影响:
.parent{
}
.left{
float: left;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
overflow: hidden;
}
.left p{width: 200px;}
table:通过内容撑开,width:0.1%,ie6 7 不兼容;
table宽度由内容决定
.parent{
display: table; width: 100%;
}
.left,.right{
display: table-cell;
}
.left{
width: 0.1%;
padding-right: 20px;
}
.left p{
width:200px;
}
flex:兼容性问题,ie10 以上;
.parent{
display: flex;
}
.left{
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
flex: 1;
}
.left p{width: 200px;}
不定宽+不定宽+自适应
.parent{
}
.left,.center{
float: l###eft;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.right{
overflow: hidden;
}
.left p,.center p{
width: 100px;
}
等分布局
利用float:
父容器增加一定宽度
关键为设置:box-sizing:border-box;
优点在于兼容性好,ie 6 7浮点兼容性问题;结构和样式有一定耦合性,这也是不足之处,改变结构需要改变样式;
.parent{
margin-left: -20px;
}
.column{
float: left;
width: 25%;
padding-left: 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
利用table:
在外侧嵌套一个盒子,扩展其宽度,然后设置平分;
table-layout:fixed;布局优先,加速布局,单元格没有设置宽度则平分;
.parent-fix{
margin-left: -20px;
}
.parent{
display: table;
width:100%;
table-layout: fixed;
}
.column{
display: table-cell;
padding-left: 20px;
}
利用flex:
item的flex都设置为1;
分布的是剩余空间;跟数量没有关系;缺点在于兼容性;
.parent{
display: flex;
}
.column{
flex: 1;
}
//选择前面还有一个column的元素
.column+.column{
margin-left:20px;
}
等高布局
table
天然等高;
flex
天然等高;
float
伪等高:
全局布局
position方案:
absolute;
Flex方案:
不设定高度宽度则为全部自适应布局;
响应式布局
缺点在于,资源上有所冗余;
响应式一般采取自适应模式
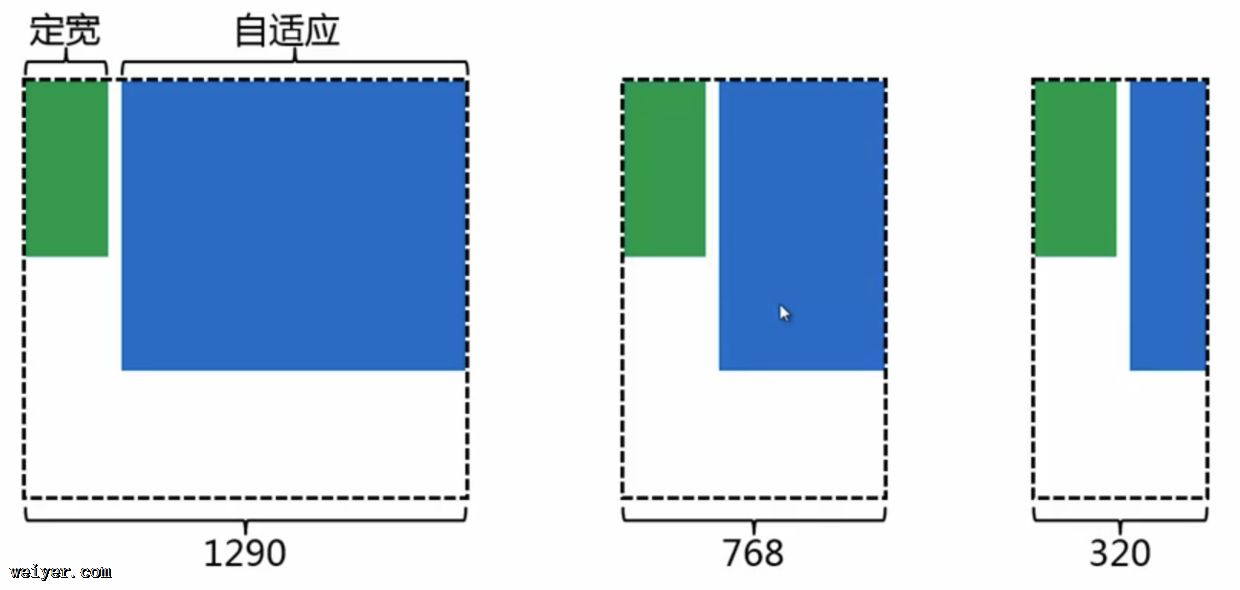
响应式布局
语法:
@media screen and (max-width:320px){
//视窗,并且最大屏幕320px;
}
功能:
改变布局,控制显示与隐藏;
相当于覆盖前面的设置;
页面优化
为什么要优化?
提升网页响应速度;对搜索引擎,屏幕阅读器友好;提高可读性,可维护性;如何优化?
减少请求 图片合并(雪碧图);CSS文件合并,少量css样式内联;避免使用import的方式引入css文件(每次单独引入一个) 减少文件大小 选择合适的图片格式 PNG(小图标)jpg(大图,色彩丰富) 压缩工具css值缩写来减少css文件大小;margin,padding,border,font,border-radius,background 省略值为0的单位;颜色值最短表示;css选择器合并文件压缩 页面性能 加载顺序 css放在head,先解析css,可以直接把样式应用在dom树上,否则容易看到没有样式的页面;js放在页面底部,很多加载逻辑需要页面加载完毕才能使用,js的加载需要时间; 减少标签数量;选择器长度:尽可能短;避免消耗性能的属性:expression,filter,border-radius,gradients;(在移动端尤其需要谨慎)图片设置宽高,防止回流重绘;所有表现用css实现; 可读性,可维护性 规范,页面开发之前指定规范,在多人协作时更加方便;语义化,对seo和屏幕阅读器更加友好;尽量避免Hack;hack尽量统一;模块化:注释:规范和模块化
规范
规范不佳,维护难;
团队应该有自己的规范;
- base lib ui业务类 album .. 文件引入 行内元素 不推荐 但是偶尔需要用外联引入 内联引入