使用SpEL配置应用程序
本章使用的依赖基本被下文件包括:
4.0.0 org.springframework.samples.service.service SpringAOPTest 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT war 1.6 UTF-8 UTF-8 <jsp.version>2.3.11.2 3.1.0 4.3.10.RELEASE 5.2.10.Final 1.2.3 1.7.25 4.12 <aspectj.version>1.8.10org.springframework spring-webmvc ${spring-framework.version} javax.servlet jstl ${jstl.version} javax.servlet javax.servlet-api ${servlet.version} provided javax.servlet.jsp javax.servlet.jsp-api ${jsp.version} provided org.springframework spring-tx ${spring-framework.version} org.springframework spring-aop ${spring-framework.version} org.springframework spring-core ${spring-framework.version} org.springframework spring-beans ${spring-framework.version} org.springframework spring-context ${spring-framework.version} org.springframework spring-expression ${spring-framework.version} org.slf4j slf4j-api ${slf4j.version} compile ch.qos.logback logback-classic ${logback.version} runtime org.hibernate hibernate-entitymanager ${hibernate.version} org.springframework spring-test ${spring-framework.version} test junit junit ${junit.version} test org.aspectj aspectjweaver ${aspectj.version}
首先在src/main/resource文件夹下创建上下文配置文件applicationContext.xml
此处将类MyBean定义成了名为show1的类,并向其中的message属性通过SpEL注入了系统属性中的用户语言。
接下来创建MyBean类。
public class MyBean {
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
然后就可以在Main类中测试配置了。
public class Main {
public static void main(String... args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
MyBean myBean = context.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(myBean.getMessage());
}
}
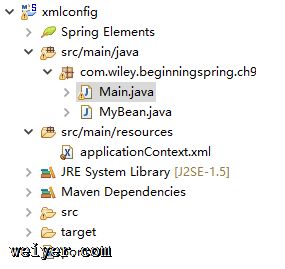
输出结果为zh,用户语言为中文。项目目录结构很简单:
事实上,也可以用注解完成配置,此时的配置类为:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wiley.beginningspring.ch9"})
public class ApplicationConfig {
}
而MyBean类需要在类定义时被定义为一个Spring Bean:
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Value("#{systemProperties['user.language']}")
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
其中message属性上通过@Value注解使用相同的SpEL语句注入了用户语言的值。
创建一个分析器
SpEL上下文中定义的表达式都应该首先被ExpressionParser解析然后被评估,该分析器对象是线程安全的。默认情况下,表达式模板以‘#’开头,‘}’结尾。分析器对象创建如下:
ExpressionParser parser = new SpELExpressionParser();
创建完分析器实例后就可以用它的parseExpression方法解析一个表达式创建一个表达式实例:
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'");
然后就可以通过它的getValue方法获得表达式评估的值:
String value = expression.getValue(String.class)
下用 SpEL 解析一个 Hello World:
public class HelloWorldTest {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void helloWorldParsedOK() {
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World!'");
String value = expression.getValue(String.class);
assertThat(value, is("Hello World!"));
}
}
测试通过。
通过SpEL调用方法
xml配置中调用方法
项目目录结构为:
首先在src/main/resource文件夹中创建applicationContext.xml文件。
该上下文文件中定义了两个类为Show的Bean。分别用字符串常量和SpEL表达式调用方法注入了值。
然后创建Show类:
public class Show {
private String instrument;
private String song;
public void setInstrument(String instrument) {
this.instrument = instrument;
}
public void setSong(String song) {
this.song = song;
}
public String guitarSong() {
return "More Than Words";
}
public void present() {
System.out.println("Playing " + song + " with instrument " + instrument);
}
}
然后创建Main方法执行程序:
public class Main {
public static void main(String... args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Show show1 = (Show) context.getBean("show1");
show1.present();
Show show2 = (Show) context.getBean("show2");
show2.present();
}
}
运行输出结果:
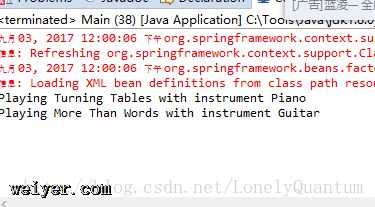
在字符串上调用方法及链接调用
public class NestedMethodInvocationStringConcatTest {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void helloParsedAndConcatenatedWithWorldAndThenLengthMethodInvoked() {
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello'.concat(' World!').length()");
Integer value = exp.getValue(Integer.class);
assertThat(value, is(12));
}
}
调用构造函数
public class ConstructorInvocationTest {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void constructorInvocationWorksOK() {
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("new Double(3.141592653589793)");
Double value = exp.getValue(Double.class);
assertThat(value, is(3.141592653589793));
}
}
调用静态方法
public class StaticConstantFieldAccessTest {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void staticConstantFieldAccessWorksOK() {
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("T(java.lang.Math).PI");
Double value = exp.getValue(Double.class);
assertThat(value, is(3.141592653589793));
}
}
使用变量和函数
可以通过context.setVariable("name",...)注册一个变量到评估上下文StandardEvaluationContext对象中,之后就可以在变量名前加#引用已经注册的变量了。
#root
可以在评估上下文中设置一个根对象,当表达式中遇到未知方法和属性时使用该对象进行查找。
public class RootVariablesTests {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void rootVariableRegisteredOK() {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setRootObject(new MyBean());
assertTrue(parser.parseExpression("#root").getValue(context) instanceof MyBean);
}
}
其中MyBean为任意类。
public class MyBean {
}
#this
提供对当前评估过程的引用。
访问一同属性和环境变量
使用前缀@来访问:
String value = parser.parseExpression("@systemEnvironment[JAVA_HOME]").getValue(context, String.class);
String value = parser.parseExpression("@systemProperties['java.version']").getValue(context, String.class);
内联列表
public class InlineListTests {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void inlineListCreatedOK() {
List value = parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3}").getValue(List.class);
assertThat(value, hasItems(1, 2, 3));
}
@Test
public void inlineListOfListsCreatedOK() {
List> value = parser.parseExpression("{{1,2},{3,4},{5,6}}").getValue(List.class);
assertThat(value, hasItems(Arrays.asList(1,2), Arrays.asList(3,4), Arrays.asList(5,6)));
}
}
注册函数
除了注册变量外还可以注册函数,并在之后调用。注册方法为context.registerFunction("name",method)
public class FunctionRegistrationTests {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void functionRegisteredOK() throws NoSuchMethodException {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.registerFunction("capitalize",
StringUtils.class.getDeclaredMethod("capitalize", new Class[] { String.class }));
String value = parser.parseExpression("#capitalize('hello')").getValue(context, String.class);
assertThat(value, is("Hello"));
}
}
SpEL运算符
关系:<, >, <=, >=, ==, !=, lt, gt, le, ge, eq, ne 算数:+, -, *, /, %, ^ 逻辑: &&, ||, !, and, or, not, between, instanceof 条件:? : (ternary), ? : (elvis) 其他类型:?.(safe navigation), ?[...](selection), , ^[...](first element), $[...](last element)
其中 instantceof 可以用来判定表达式是否为某个类的实例,如"'Hello' instanceof T(String)"返回一个true值的Boolean变量。
安全导航运算符用于在嵌套属性上进行导航,使未初始化的属性返回null值而不是抛出SpelEvaluationException。如
public class SafeNavigationOperatorsTest {
ExpressionParser p;
@Before
public void setup() {
p = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void safeNavigationOperatorsWorkOK() {
Employee employee = new Employee("Mert");
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(employee);
assertThat(p.parseExpression("Address?.Name").getValue(context, String.class), is(nullValue()));
}
}
利用之前提到的#this还可以进行集合选择与投影将其转换为另一个集合。
@Test
public void collectionSelectedOK() {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setRootObject(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9));
List evenNumbers = parser.parseExpression("#root.?[#this%2 == 0 ?: false]").getValue(context, List.class);
assertThat(evenNumbers, hasItems(2, 4, 6, 8));
}
其中#this用来遍历集合中元素。
还可以通过![…]将一个集合投影到另一个集合,如下:
public class Worker {
private String name;
private Country birthPlace;
public Worker(String name, Country birthPlace) {
this.name = name;
this.birthPlace = birthPlace;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Country getBirthPlace() {
return birthPlace;
}
}
public enum Country {
TR,
USA,
DE
}
投影Worker到Country:
@Test
public void collectionProjectedOK() {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setRootObject(Arrays.asList(
new Worker("Mert", Country.DE),
new Worker("Funda", Country.TR),
new Worker("Tugce", Country.USA)));
List birthPlaces = parser.parseExpression("#root.![#this.birthPlace]").getValue(context, List.class);
assertThat(birthPlaces, hasItems(Country.TR, Country.USA, Country.DE));
}
使用SpEL中的实用工具
访问Spring Bean
在Bean名称前添加@来访问
public class SpringBeanAccessTests {
ExpressionParser parser;
@Before
public void setup() {
parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
}
@Test
public void springBeanAccessWorksOK() {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setBeanResolver(new BeanFactoryResolver(new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationConfig.class)));
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("@myBean.sayHello()");
String value = exp.getValue(context, String.class);
assertThat(value, is("Hello!"));
}
}
@Component
public class MyBean {
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello!";
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wiley.beginningspring.ch9"})
public class ApplicationConfig {
}
使用spring.tld中的该标签可以将评估值显示到JSP页面或为变量分配值。