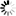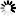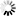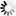简单说一说数据结构——集合,迄今为止,我们已经学习了数组(列表)、栈、队列和链表(及其变种)等顺序数据结构。
这一节我们讲讲集合。集合的定义是由一组无序且唯一(即不能重复)的项组成的。不包含任何元素的集合就叫做空集。上高中那会,我们都接触过集合,其中一些概念比如交集、并集、差集等等。
ECMAScript6也实现了集合这种数据结构——Set类。而我们用ECMAScript5来实现。也可以为看Set时做铺垫。
首先,集合Set类的骨架是
function Set(){
var items = {};
}
与之前不同的是,这里使用的是对象而不是数组来表示集合。因为对象和集合有一个共同点,Javascript不允许一个键指向两个不同的属性,也保证了集合里的元素都是唯一的。
集合Set类中有一些可用的方法:
add(value):向集合添加一个新的项。
remove(value):从集合中移除一个值。
has(value):判断集合中是否存在某个值。
clear():移除集合中所有的项。
size():返回集合中所包含元素的数量。
values():返回一个包含集合中所有值的数组。
实现起来借助对象也是非常easy的:
this.has = function(value){
return items.hadOwnProperty(value); //return value in items;
};
this.add = function(value){
if(!this.has(value)){
items[value] = value;
return true;
}
return false;
};
this.remove = function(value){
if(this.has(value)){
delete items[value];
return true;
}
return false;
};
this.clear = function(){
items = {};
};
// this.size = function(){
// return Object.keys(items).length;
// };
this.sizeLegacy = function(){
var count = 0;
for(var prop in items){
if(items.hadOwnProperty(prop)){
count++;
}
}
return count;
};
// this.values = function(){
// return Object.keys(items);
// }
this.valuesLegacy = function(){
var keys = [];
for(var key in items){
if(items.hadOwnProperty(key)){
keys.push(key);
}
}
return keys;
};
以上代码值得注意的点有:在has方法中,hasOwnProperty函数会返回对象是否有某个特定属性。有就返回true,没有就返回false。其次在size方法中,提供了两种方式。第一种方式是利用keys函数,它返回一个包含给定对象所有属性的数组。支持该方法的浏览器有IE9+、Firefox4+、Chrome5+、Opera12+和Safari5+。要使size方法适用所有浏览器,那么就使用sizeLegacy函数。values函数同理。
了解完集合的基本概念和操作。下面讲一讲集合之间的关系及操作:
并集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中所有元素的新集合。
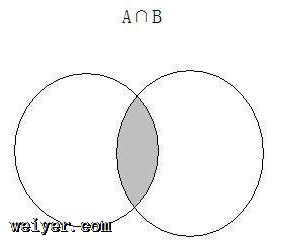
交集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中共有元素的新集合。
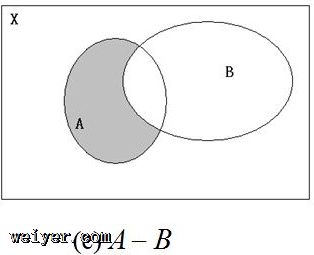
差集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含所有存在于第一个集合且不存在于第二个集合的元素的新集合。
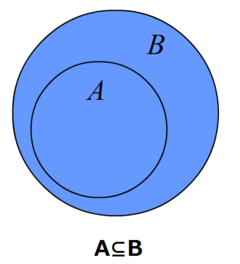
子集:验证一个给定集合是否是另一个集合的子集。
并集用一张图表示:
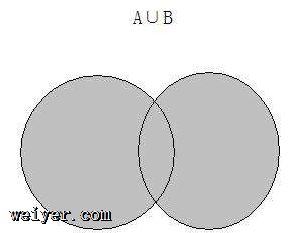
this.union = function(otherSet){
var unionSet = new Set();
var values = this.values();
for(var i = 0 ; i < values.length ; i++){
unionSet.add(values[i]);
}
for(var i = 0 ; i < otherSet.length ; i++){
unionSet.add(otherSet[i]);
}
return unionSet;
};
交集用一张图表示:
this.intersection = function(){
var intersectionSet = new Set();
var values = this.values();
for(var i = 0 ; i < values.length ; i++){
if(otherSet.has(values[i])){
intersectionSet.add(values[i]);
}
}
return intersectionSet;
};
差集用一张图表示
this.difference = function(otherSet){
var differenceSet = new Set();
var values = this.values();
for(var i = 0 ; i < values.length ; i++){
if(!otherSet.has(values[i])){
differenceSet.add(values[i]);
}
}
return differenceSet;
};
最后一个子集:
this.subset = function(otherSet){
if(this.size() > otherSet.size()){
return false;
}else{
var values = this.values();
for(var u = 0 ; i < values.length ; i++){
if(!otherSet.has(values[i])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
集合讲到这里也就完了,还是比较简单的一种结构。