我们在使用AJAX来做服务器端和客户端交互的时候,一般的做法是让服务器端返回一段JSON字符串,然后在客户端把它解析成javascript对象。解析时用到的方法一般是eval或者new function,而目前IE8和Firefox3.1又内置了原生的JSON对象(据说会有一定的性能提升)。那我们在实际使用的时候怎样从这三种方法(因为性能问题,不考虑用javascript实现的解析)里面来选择呢?面对众多的浏览器,哪种方式的性能是最好的呢?
一、测试方法
1、首先指定测试次数及JSON字符串
1: var count = 10000, o = null, i = 0, jsonString = '{"value":{"items": [{"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}]},"error":null}';
2、循环解析并记录时间
1: var beginTime = new Date();
2: for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
3: o = eval( "(" + jsonString + ")" );
4: }
5: Console.output( "eval:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
1: var beginTime = new Date();
2: for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
3: o = new Function( "return " + jsonString )();
4: }
5: Console.output( "new Function:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
1: if ( typeof JSON !== "undefined" ) {
2: var beginTime = new Date();
3: for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
4: o = JSON.parse( jsonString ); }
5: Console.output( "native:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
6: } else {
7: Console.output( "native:not support!" );
8: }
二、测试对象
选择目前主流的浏览器(不考虑Maxthon一类的外壳),包括IE6、7、8,Firefox2、3、3.1,Chrome,Opera及Safari3、4。
三、测试环境
T9300 CPU + 4G RAM + Windows2003,其中IE8使用的是Vista的环境,IE7在另外一台工作机(2G CPU + 2G RAM + Windows2003),考虑到主要是测试浏览器客户端的性能,结果的误差应该能够接受。
四、测试结果
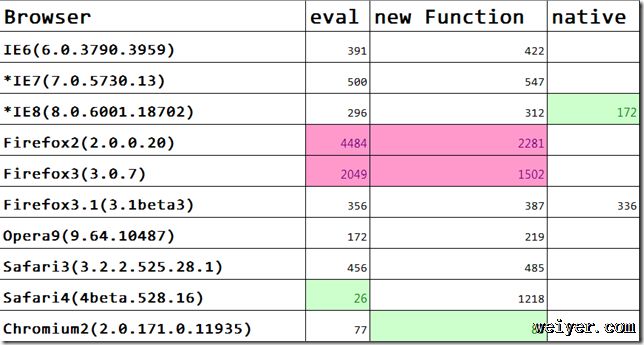
*数值越小越好
*在当前列中绿色背景的表示性能最好,红色性能最差
1、Firefox2、3全部垫底,IE6的性能优于IE7(可能和机器不一致有关),Chrome和Safari4的性能远远超出其它浏览器。
2、不同的浏览器下eval和new Function的性能不一致,总的来说eval更好,但Firefox下new Function的性能是eval的一倍,为了更好的兼容各个浏览器,我们把对JSON的解析单独封装成一个对象来处理:
1: var __json = null;
2: if ( typeof JSON !== "undefined" ) {
3: __json = JSON;
4: }
5: var browser = Browser;
6: var JSON = {
7: parse: function( text ) {
8: if ( __json !== null ) {
9: return __json.parse( text );
10: }
11: if ( browser.gecko ) {
12: return new Function( "return " + text )();
13: }
14: return eval( "(" + text + ")" )
15: }
16: };
17: var beginTime = new Date();
18: for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
19: o = JSON.parse( jsonString ); }
20: Console.output( "wrapper:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
加入Wrapper后的结果:
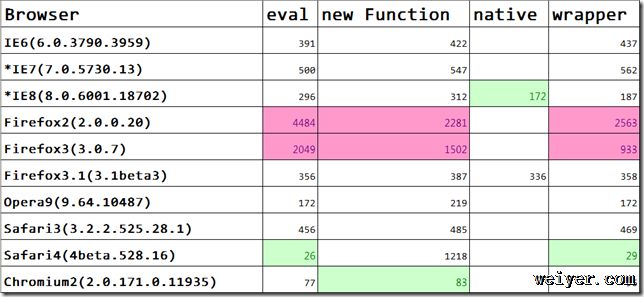
由于涉及到调用对象的开销,封装后JSON对象会比单独调用更慢,但它能保证在各个浏览器下使用最适合的方法。
五、结论
解析Json字符串时,不同的浏览器选择不同的方法:
- IE6、7使用eval
- IE8使用原生的JSON对象
- Firefox2、3使用new Function
- Safari4使用eval
- 其它浏览器下eval和new Function的性能基本一致
如果有不同意见欢迎拍砖:)
附:全部代码

 Code
Code
DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Parse JsonStringtitle>
head>
<body>
<div id="consoleRegion">div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//yui
var Browser = function() {
var o = {
ie: 0,
opera: 0,
gecko: 0,
webkit: 0
};
var ua = navigator.userAgent, m;
if ( ( /KHTML/ ).test( ua ) ) {
o.webkit = 1;
}
// Modern WebKit browsers are at least X-Grade
m = ua.match(/AppleWebKit\/([^\s]*)/);
if (m&&m[1]) {
o.webkit=parseFloat(m[1]);
}
if (!o.webkit) { // not webkit
// @todo check Opera/8.01 (J2ME/MIDP; Opera Mini/2.0.4509/1316; fi; U; ssr)
m=ua.match(/Opera[\s\/]([^\s]*)/);
if (m&&m[1]) {
o.opera=parseFloat(m[1]);
} else { // not opera or webkit
m=ua.match(/MSIE\s([^;]*)/);
if (m&&m[1]) {
o.ie=parseFloat(m[1]);
} else { // not opera, webkit, or ie
m=ua.match(/Gecko\/([^\s]*)/);
if (m) {
o.gecko=1; // Gecko detected, look for revision
m=ua.match(/rv:([^\s\)]*)/);
if (m&&m[1]) {
o.gecko=parseFloat(m[1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return o;
}();
var Console = {
consoleRegion: null,
getRegion: function() {
if ( this.consoleRegion === null ) {
this.consoleRegion = document.getElementById( "consoleRegion" );
}
return this.consoleRegion;
},
output: function( text ) {
this.getRegion().innerHTML += "
" + text;
}
};
//test code
var count = 10000, o = null, i = 0, jsonString = '{"value":{"items": [{"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}, {"x":1,"y":2,"z":3}]},"error":null}';
//eval
var beginTime = new Date();
for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
o = eval( "(" + jsonString + ")" );
}
Console.output( "eval:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
//new Function
beginTime = new Date();
for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
o = new Function( "return " + jsonString )();
}
Console.output( "new Function:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
//native
if ( typeof JSON !== "undefined" ) {
beginTime = new Date();
for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
o = JSON.parse( jsonString );
}
Console.output( "native:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
} else {
Console.output( "native:not support!" );
}
//wrapper
var __json = null;
if ( typeof JSON !== "undefined" ) {
__json = JSON;
}
var browser = Browser;
var JSON = {
parse: function( text ) {
if ( __json !== null ) {
return __json.parse( text );
}
if ( browser.gecko ) {
return new Function( "return " + text )();
}
return eval( "(" + text + ")" )
}
};
beginTime = new Date();
for ( i = 0; i < count; i++ ) {
o = JSON.parse( jsonString );
}
Console.output( "wrapper:" + ( new Date() - beginTime ) );
//alert( o.value.items[0].z );
script>
body>
html>